Automation equipment is an integral part of modern industrial operations. It refers to a wide range of machinery and devices that are designed to perform specific tasks with minimal or no human intervention. With the advent of electricity and the development of new technologies, the use of automation equipment has expanded rapidly. Today, automation equipment is used in a wide range of industries such as manufacturing, healthcare, agriculture, logistics and warehousing, construction, and energy. Read More…
A recognized leader in automated assembly products. Stay competitive with Dixon's robotic screwdrivers, auto-fed screw & nut drivers, auto-fed part placers, parts feeding systems & assembly cells, including robotic assembly & vision. Every Dixon product is manufactured to assure accuracy & dependability for repetitive assembly. Dixon supports Machine Integrators with assembly products & stations. ...

Invio Automation is a leading comprehensive AGV, AMR, and robotics integrator with 10 engineering and support sites throughout North America. We specialize in heavyweight and assembly line applications.

Advent design has been in business for over 35 years providing custom automation solutions, engineering, integration solutions and machine safety services. Contact us today to discuss your project needs and see how we can help you achieve your goals.

Since 1982, Isotech has been a leader in the automation equipment industry. You can trust the accuracy of our solutions. Our experts at Isotech are always available to assist you with your needs. Feel free to contact us today to learn more information!

Del-Tron Precision is your one-stop shop for ball & crossed roller slides, multi-axis positioning and motor-ready lead screw stages, air actuators, recirculating slide guides and crossed roller rail sets. Custom linear slides are available.

More Assembly Machinery Manufacturers
Get a quote from leading Assembly Machinery Manufacturers.
What are the Types of Automation & Industrial Assembly Equipment?
Answer: Automation equipment encompasses a diverse spectrum of advanced technologies designed to transform industrial manufacturing, streamline assembly processes, and boost efficiency across countless sectors. The deployment of state-of-the-art assembly machinery and industrial automation equipment has become a cornerstone for manufacturers seeking to enhance productivity, reduce operating costs, ensure product consistency, and meet evolving market demands.
Below is a comprehensive overview of the most prevalent types of automation and assembly machinery found in modern factories, production environments, and automated facilities. If you’re considering upgrading your operations, explore these automation solutions to identify the best fit for your specific applications:
- Robotic Arms
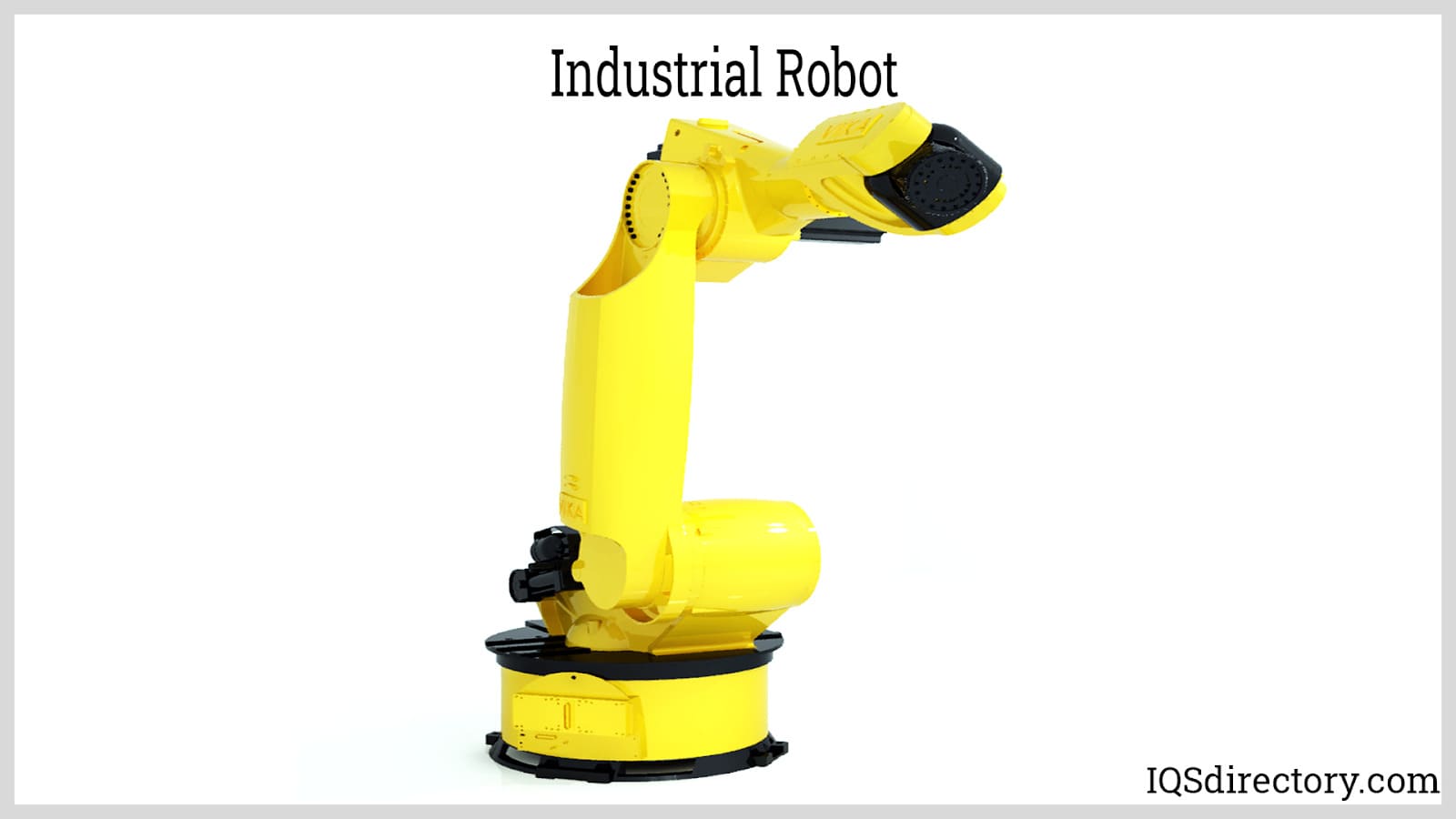
Programmable, multi-axis robotic arms automate repetitive manufacturing tasks such as welding, industrial assembly, and material handling. Automotive production lines frequently deploy robotic arms like FANUC’s R-2000iC for high-precision welding and heavy lifting, supporting payloads up to 270 kg. These industrial robots are integral in automotive, electronics, and heavy machinery manufacturing for tasks that demand accuracy, speed, and repeatability.
Key search queries: “robotic arm applications”, “industrial robots for manufacturing”, “robotic assembly solutions” - Conveyors
Belt, roller, and chain-driven conveyor systems are foundational in automated material handling. These systems efficiently transport goods and components, with large-scale warehouses and distribution hubs (e.g., Amazon) relying on conveyor automation for rapid order fulfillment and streamlined logistics. Conveyors support continuous production flow, minimize bottlenecks, and integrate seamlessly with packing, sorting, and inspection machinery.
Buyer search intent: “best conveyor systems for warehouse automation”, “conveyor integration with robotics” - Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs)
PLCs—such as Siemens’ S7-1200—are the intelligent control centers of automation, managing assembly machinery, production lines, and process automation through programmable instructions. PLCs are essential for automating tasks in manufacturing, food processing, HVAC, and other industrial operations. Learn more about assembly lines.
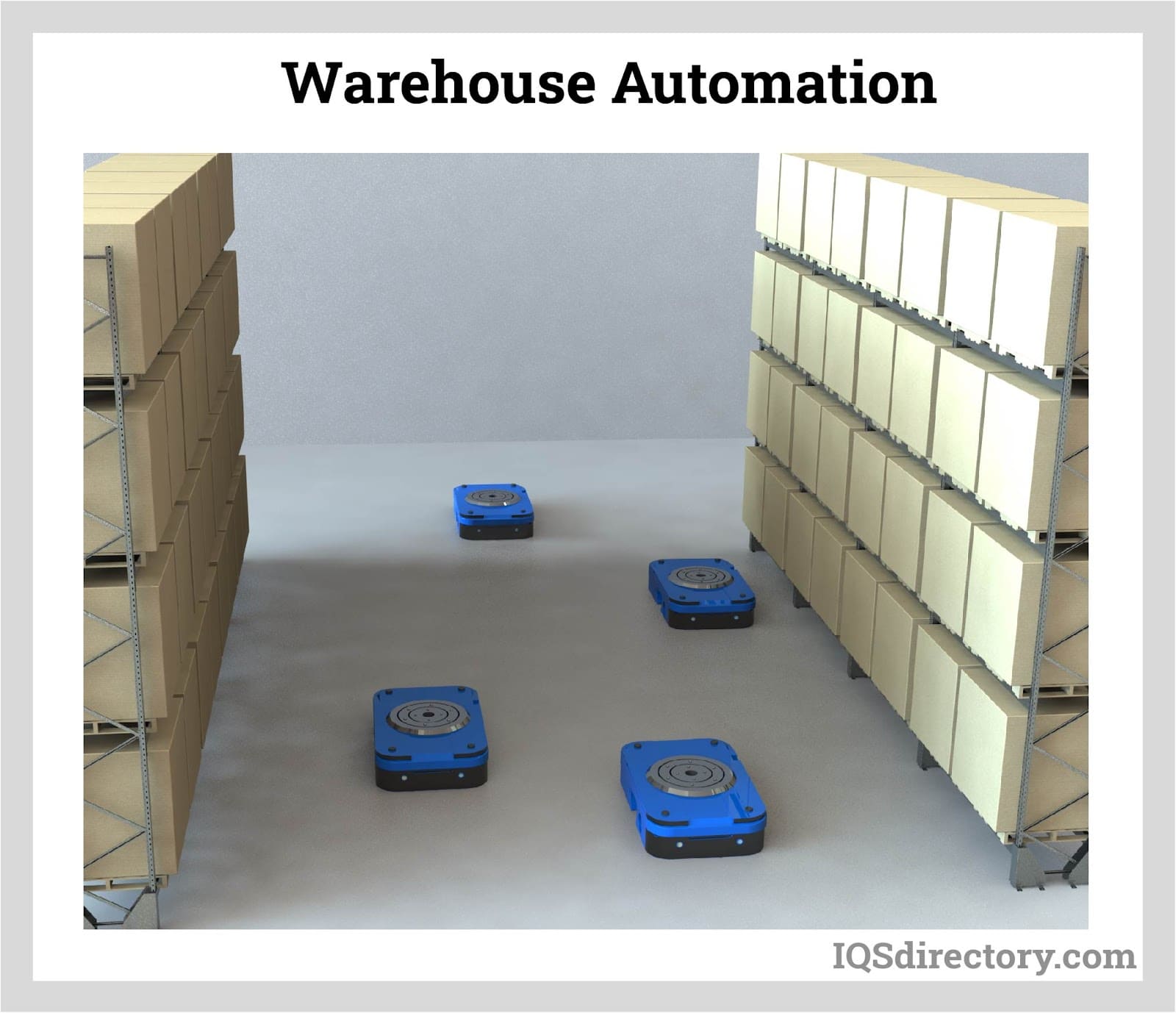
Common user questions: “What is a PLC used for in manufacturing?”, “How to program a PLC for assembly automation?” - Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs)
Driverless, sensor-guided AGVs autonomously transport materials throughout facilities. Manufacturers deploy AGVs like those from JBT to move components between workstations, reducing manual handling, improving efficiency, and lowering labor costs in automated warehouses. AGVs are instrumental in lean manufacturing, just-in-time production, and facilities seeking increased safety and flexibility.
Related queries: “AGV vs AMR for warehouse automation”, “benefits of automated guided vehicles” - CNC Machines
Computer Numerical Control (CNC) machines—including lathes, mills, and routers—enable automated, high-precision cutting, drilling, and shaping of metals and plastics. CNC technology is vital in aerospace, automotive, and electronics industries for producing complex components with exacting tolerances. These machines can operate 24/7 with minimal supervision, ensuring consistent output.
User search queries: “types of CNC machines”, “CNC machining for precision manufacturing”, “CNC automation benefits” - Sensors and Actuators
Sensors (such as photoelectric, temperature, and pressure sensors) monitor real-time changes on production lines, while actuators (motors, pistons, valves) trigger responsive actions. These automation components work together to maintain efficient, reliable operations in sectors like packaging and bottling. Advanced sensors enable predictive maintenance, quality control, and process optimization.
Questions to consider: “How do sensors improve automation?”, “Sensor types for industrial robots” - Industrial Robots
Beyond traditional robotic arms, industrial robots include pick-and-place robots, SCARA robots, and collaborative “cobots” (e.g., Universal Robots’ UR5), which safely work alongside humans. These solutions enhance productivity in electronics, packaging, and light manufacturing.
Buyers also ask: “What is a cobot?” “How do collaborative robots impact productivity?”
Supporting Automation Equipment and Technologies
- Vision Systems & Quality Inspection
Machine vision systems use cameras and image processing to inspect components for defects, verify assembly quality, and guide robotic arms. They are indispensable in electronics, automotive, and food & beverage sectors for automated quality assurance.
Common searches: “machine vision for assembly lines”, “automated inspection systems” - Automated Palletizers & Depalletizers
Automated palletizing systems stack finished products onto pallets, while depalletizers unload them for further processing. These machines improve throughput in distribution centers and packaging plants.
Search focus: “automated palletizer ROI”, “robotic palletizing systems” - Material Handling Robots
Specialized robots designed for picking, packing, sorting, and moving goods within warehouses and manufacturing plants. They reduce manual labor and enhance safety.
Relevant queries: “material handling automation”, “pick and place robot applications” - Smart Factory Systems & IIoT Platforms
Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) platforms connect automation devices, enabling real-time data collection, remote monitoring, and predictive analytics. Smart factory solutions help manufacturers optimize every aspect of production.
User intent: “IIoT in manufacturing”, “smart factory automation benefits”
Considerations with Automation Equipment
When planning to invest in industrial automation equipment, manufacturers must weigh several crucial factors that directly influence operational success, cost-effectiveness, and long-term scalability.
- Workforce Impact: Automation can lead to job displacement as repetitive manual tasks become automated. However, it also creates demand for skilled technicians, robotics engineers, and automation programmers.
- Upfront Costs: The initial investment in automation machinery, software, and system integration can be significant. Calculating the total cost of ownership—including installation, training, and ongoing maintenance—is essential for accurate ROI projections.
- Integration Complexity: Ensuring seamless integration between new automation equipment and existing systems often requires custom engineering solutions and close collaboration with experienced automation integrators.
- Maintenance & Support: Automated systems require regular preventative maintenance, software updates, and access to responsive technical support to maximize uptime.
- Cybersecurity Risks: As factories adopt connected automation equipment, safeguarding against cyber threats becomes increasingly important. Implementing robust security protocols and regular risk assessments is non-negotiable.
Looking to learn more? What are the hidden costs of automation? How can you balance automation with workforce development? Explore our in-depth guides for answers to these and other frequently asked questions.
Advantages of Automation Equipment
Despite the challenges, the adoption of automation and assembly machinery delivers transformative benefits for manufacturers, logistics providers, and industrial operations worldwide:
- Increased Throughput & Productivity: Automated systems run continuously—24/7 if needed—substantially increasing production volumes and reducing cycle times. This is crucial for high-volume manufacturing sectors such as automotive and electronics.
- Superior Quality & Consistency: Automation reduces the risk of human error, enabling precise, repeatable processes that result in uniform product quality and fewer defects. Machine vision systems further enhance quality control.
- Cost Reduction: Automation minimizes labor costs, reduces scrap and rework, and improves resource utilization. Over time, these savings far outweigh initial investment costs.
- Enhanced Workplace Safety: Automated equipment takes over hazardous tasks—such as heavy lifting, toxic material handling, or repetitive motion—protecting workers from injury and reducing workers’ compensation claims.
- Scalability & Flexibility: Modular automation systems can be expanded or reconfigured as demand changes, allowing companies to respond quickly to market shifts.
- Data-Driven Decision Making: Connected automation systems provide real-time production data, enabling continuous improvement, predictive maintenance, and agile supply chain management.
Not sure if automation is right for your operation? What are the ROI benchmarks for automation in your industry? Which processes should be automated first for maximum impact? Use our decision tools or contact industry experts for tailored advice.
Sustainability and Positive Environmental Impact
Modern automation equipment is instrumental in advancing sustainable manufacturing practices and reducing environmental footprints. Here’s how automation supports green initiatives:
- Energy Efficiency: Advanced robotic systems, servo motors, and smart control algorithms minimize energy consumption by optimizing machine cycles and reducing idle times.
- Waste Reduction: Automated dispensing and measurement systems ensure precise material usage, reducing overproduction, scrap, and raw material waste.
- Predictive Maintenance: Sensor-driven predictive maintenance prevents unexpected breakdowns, minimizing downtime and material loss while extending equipment lifespan.
- Compliance: Automation helps companies meet regulatory requirements for emissions, traceability, and workplace safety, supporting ISO 14001 and other environmental certifications.
Searching for “sustainable manufacturing solutions” or “energy-efficient automation equipment”? Learn how leading manufacturers are leveraging automation for eco-friendly operations.
Adapting Your Workforce to Automation
As automation technologies proliferate, the workforce must evolve to meet new technical demands. Upskilling and reskilling are critical to ensure employees thrive in increasingly automated environments. Here’s how organizations can adapt:
- Training & Certification: Invest in training programs for robotics operation, PLC programming, equipment maintenance, and data analytics. Certification programs from industry leaders and technical colleges are valuable assets.
- Collaboration with Education Providers: Partner with universities, technical schools, and online education platforms to deliver targeted courses and apprenticeships.
- Continuous Learning Culture: Foster a culture where employees regularly update skills to keep pace with evolving automation and digital transformation trends.
- Job Redesign: Redefine job roles to focus on oversight, troubleshooting, and process improvement rather than manual, repetitive labor.
- Public-Private Partnerships: Engage in workforce development initiatives that bridge skills gaps and prepare future talent pipelines in robotics, AI, and mechatronics.
Wondering how to future-proof your workforce? What skills will be in demand in tomorrow’s smart factories? How can you retain top talent in an automated environment? Explore our workforce transformation resources for actionable insights.
Applications of Automation Equipment
Automation equipment is foundational to modern manufacturing, facilitating higher output, reduced defects, and consistent product quality. Explore the wide range of industrial automation applications across multiple industries:
- Manufacturing: Automated assembly lines, robotic welding, CNC machining, and vision inspection systems drive mass production in automotive, aerospace, consumer electronics, and medical device sectors.
- Logistics & Warehousing: Automated sorting systems, conveyors, and AGVs accelerate order fulfillment, improve inventory accuracy, and optimize supply chain management for e-commerce and retail distribution centers.
- Agriculture: Agricultural automation—using drones, autonomous tractors, and robotic harvesters—streamlines planting, irrigation, and harvesting, increasing yields and lowering costs.
- Healthcare: Healthcare automation includes robotic surgery, automated diagnostics, and pharmacy dispensing systems, improving patient outcomes and operational efficiency.
- Construction: Automated equipment and drones support site surveying, risk assessment, 3D printing, and productivity monitoring, while enhancing worker safety and project delivery speed.
- Food & Beverage: Automated bottling, packaging, and inspection systems ensure food safety, reduce contamination risks, and enable traceability throughout the supply chain.
Want to learn more? What are the top automation trends in your industry? How do leading companies leverage automation for competitive advantage? Check our case studies and industry analysis for examples and best practices.
How will AI affect the future of automation equipment?
Answer:
Artificial intelligence (AI) is revolutionizing the automation equipment industry by making industrial systems smarter, more flexible, and adaptive. Integrating AI into automation tools—such as robotic arms, PLCs, AGVs, and industrial robots—enables advanced analytics, real-time decision-making, and autonomous process optimization across sectors.
AI-powered automation delivers unprecedented precision and productivity. For example, robotic arms with machine learning algorithms can adjust weld angles in real time based on visual data, minimizing defects and maximizing efficiency. Predictive maintenance systems use AI to analyze sensor data from CNC machines and conveyors, identifying wear patterns and preventing costly breakdowns, which can save up to 30% on repairs (McKinsey).
Intelligent AGVs—like those from Otto Motors—navigate complex warehouse environments by processing real-time sensor data, dynamically avoiding obstacles and adjusting routes to changing logistics needs. AI-enhanced PLCs autonomously optimize production line parameters, reduce energy usage, and improve overall operational efficiency.
AI also reshapes labor dynamics, with collaborative robots (cobots) learning from human operators for complex assembly, enabling flexible automation in electronics and automotive manufacturing. While AI integration requires upfront investment and robust cybersecurity measures, its advantages are compelling: greater productivity, improved safety, and enhanced sustainability. According to Deloitte, AI-driven automation could add $15 trillion to global GDP by 2030. Ready to discover how AI-powered automation can advance your industry? Let’s explore your options.
Each automation technology serves a specialized function—PLCs for process control, robotics for precision work, and AGVs for automated material transport.
Want to dive deeper? How is AI changing industrial automation? What are the best practices for implementing AI-powered equipment? Visit our resource hub for the latest insights and implementation guides.
Choosing Appropriate Automation Equipment
Selecting the right automation equipment for your facility is a strategic process that impacts productivity, cost, and long-term scalability. Consider these steps to guide your automation investment:
- Identify Automation Objectives: Define your goals—such as increasing output, reducing operational costs, or elevating product quality. Specify the processes to automate and set measurable targets.
- Assess Operational Requirements: Analyze the complexity, production volume, available floor space, safety standards, and regulatory requirements of your application.
- Conduct Feasibility Studies: Evaluate total cost of ownership, including acquisition, integration, installation, maintenance, and staff training. Compare these costs with the anticipated efficiency and ROI.
- Research Industry Solutions: Explore current automation technologies and equipment options, focusing on performance, compatibility, scalability, and reliability. Leverage industry publications, trade shows, and expert consultations to stay informed.
- Consult with Vendors and System Integrators: Engage experienced automation suppliers and integrators who understand your industry’s requirements. Utilize their expertise for custom solutions, system design, and on-site evaluations.
- Evaluate Flexibility and Future Scalability: Choose modular, reconfigurable systems that can adapt as your production needs grow or change.
- Pilot and Validate Solutions: Whenever possible, conduct real-world trials to test the equipment’s performance, gather user feedback, and ensure it meets your operational demands.
- Ensure Comprehensive Training and Support: Work with equipment suppliers that offer robust training programs and responsive technical support to maximize system uptime and operator proficiency.
By following these guidelines, you can select automation equipment that aligns with your business objectives, optimizes your production process, and supports future growth.
Need help comparing automation systems? How do you calculate automation ROI? Which technologies provide the fastest payback? What are the most reliable automation brands? Use our comparison tools or consult with our listed experts for personalized recommendations.
Choosing the Correct Automation Equipment Supplier
Selecting the right automation equipment supplier is crucial to successful system integration and long-term support. Our extensive directory of automation equipment manufacturers features in-depth business profiles detailing each supplier’s core competencies, engineering specialties, and solution offerings. Each profile includes a direct contact form for inquiries or requests for quotes.
Utilize our proprietary website previewer to quickly evaluate supplier capabilities and focus areas, helping you efficiently identify the best fit for your project.
Our streamlined RFQ (Request for Quote) form allows you to contact multiple automation equipment suppliers at once, simplifying the comparison process. This ensures you find the most suitable partner to provide reliable, cost-effective automation solutions tailored to your organization’s unique operational needs.
Ready to start your automation journey? Who are the top automation equipment manufacturers? How do you request a quote for custom assembly machinery? What should you ask potential automation suppliers? Visit our supplier directory and resource center to get started.
Conclusion: Maximizing Success with Industrial Automation and Assembly Machinery
Industrial automation equipment and assembly machinery are at the heart of modern manufacturing, logistics, and process industries. By leveraging the right combination of robotics, conveyors, PLCs, AGVs, machine vision, and AI-driven solutions, organizations can dramatically improve efficiency, product quality, sustainability, and profitability. Understanding your specific automation needs, evaluating technologies, and selecting the right suppliers are critical steps toward building a future-ready, resilient, and competitive operation.
Whether you’re seeking to automate a single process or overhaul your entire production line, our resources, supplier directory, and expert guides can help you research, evaluate, and implement the best automation equipment for your unique requirements. Request a quote today or browse our manufacturer listings to take the next step in your automation journey.
What are the main types of automation and industrial assembly equipment?
Automation and industrial assembly equipment includes robotic arms, conveyors, programmable logic controllers (PLCs), automated guided vehicles (AGVs), CNC machines, sensors and actuators, and industrial robots such as pick-and-place robots and collaborative cobots. Supporting technologies include vision systems, automated palletizing systems, material handling robots, and Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) platforms for smart factory integration.
What are the main advantages of using automation equipment in manufacturing?
Automation equipment increases throughput and productivity, enhances quality and consistency, reduces operational costs, improves workplace safety, scales flexibly to changing demands, and supports data-driven decision-making. Automated systems reduce human error, allow for continuous operation, and minimize labor costs while ensuring quality control.
How does automation support sustainability and environmental goals?
Modern automation equipment helps achieve sustainability goals by improving energy efficiency, reducing material waste, enabling predictive maintenance, and supporting regulatory compliance. Technologies such as smart control algorithms, automated measurement systems, and sensor-based monitoring reduce energy consumption, minimize production scrap, and extend equipment lifespan, all of which contribute to lowering environmental footprints.
What are the key considerations when investing in automation equipment?
Important considerations include workforce impact and training, upfront costs and total cost of ownership, complexity of integration with existing systems, ongoing maintenance and support requirements, and addressing cybersecurity risks. Thorough feasibility studies and careful planning help ensure successful automation projects with high return on investment.
How will artificial intelligence (AI) impact the future of automation equipment?
AI is transforming automation by enabling smarter, adaptive, and self-optimizing industrial systems. AI integration improves precision, enables real-time decision-making, predictive maintenance, and autonomous optimization of processes. AI-driven robotics, smart AGVs, and PLCs are reshaping factory operations, improving productivity, flexibility, and safety, and are expected to add significant value to global industries in the coming years.
What industries benefit from automation equipment and how is it applied?
Automation equipment is widely used in manufacturing, logistics and warehousing, agriculture, healthcare, construction, and food and beverage sectors. Applications include automated assembly lines, robotic welding, vision inspection, order fulfillment, agricultural processing, healthcare diagnostics, and packaging, resulting in higher output, improved accuracy, and better safety across industries.
How can manufacturers adapt their workforce to increasing automation?
Manufacturers can upskill workers through targeted training on robotics, PLCs, and digital technologies, foster collaboration with educational institutions, promote continuous learning, redesign job roles for oversight and process improvement, and participate in workforce development programs. This approach enables employees to thrive alongside new automation technologies and ensures long-term competitiveness.
How should businesses select the right automation equipment and supplier?
Businesses should assess operational requirements, define automation objectives, evaluate total cost of ownership, research available technologies, and consult with experienced vendors and integrators. Selecting suppliers with strong technical support, expertise in system integration, and a track record in relevant industries ensures the best fit for custom automation solutions.




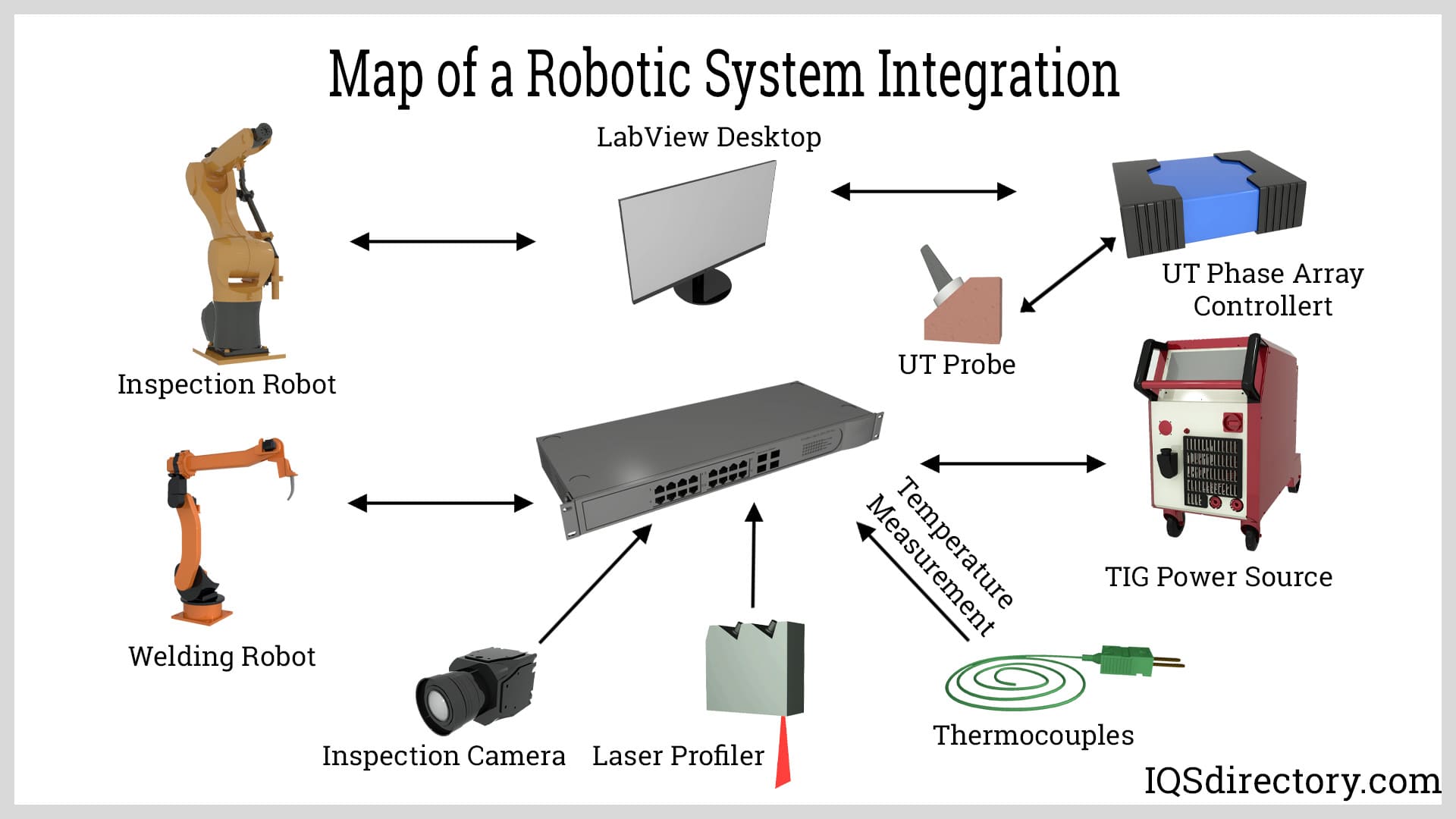


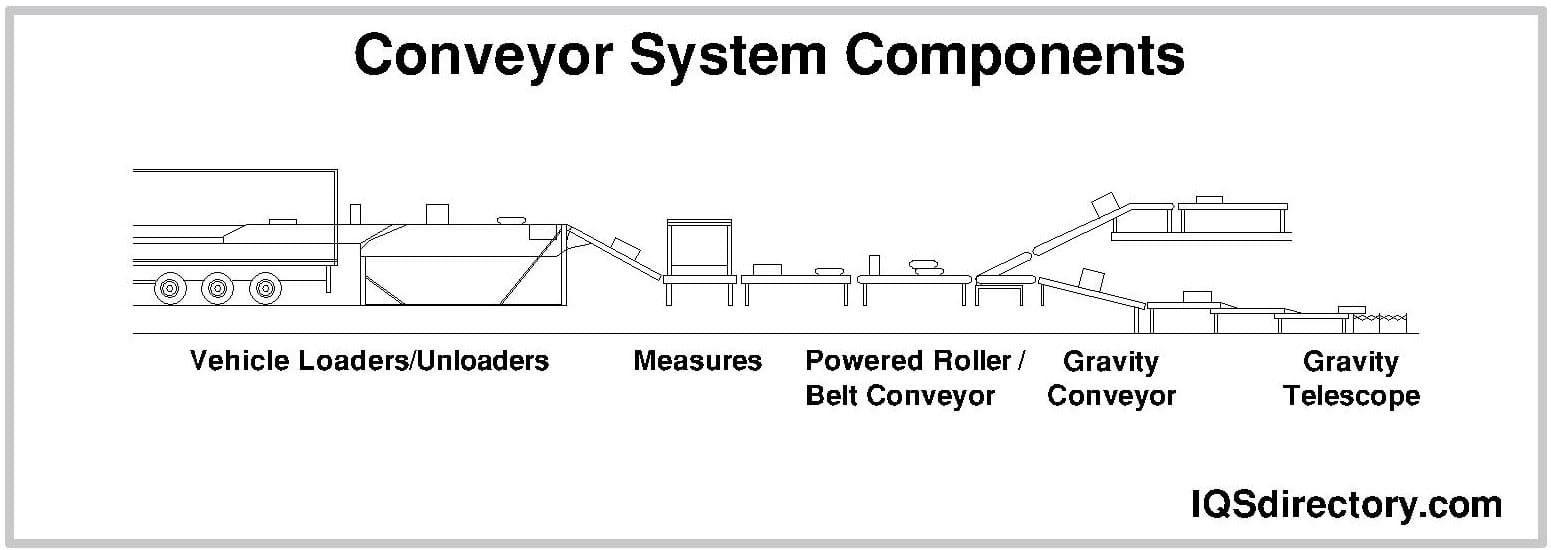
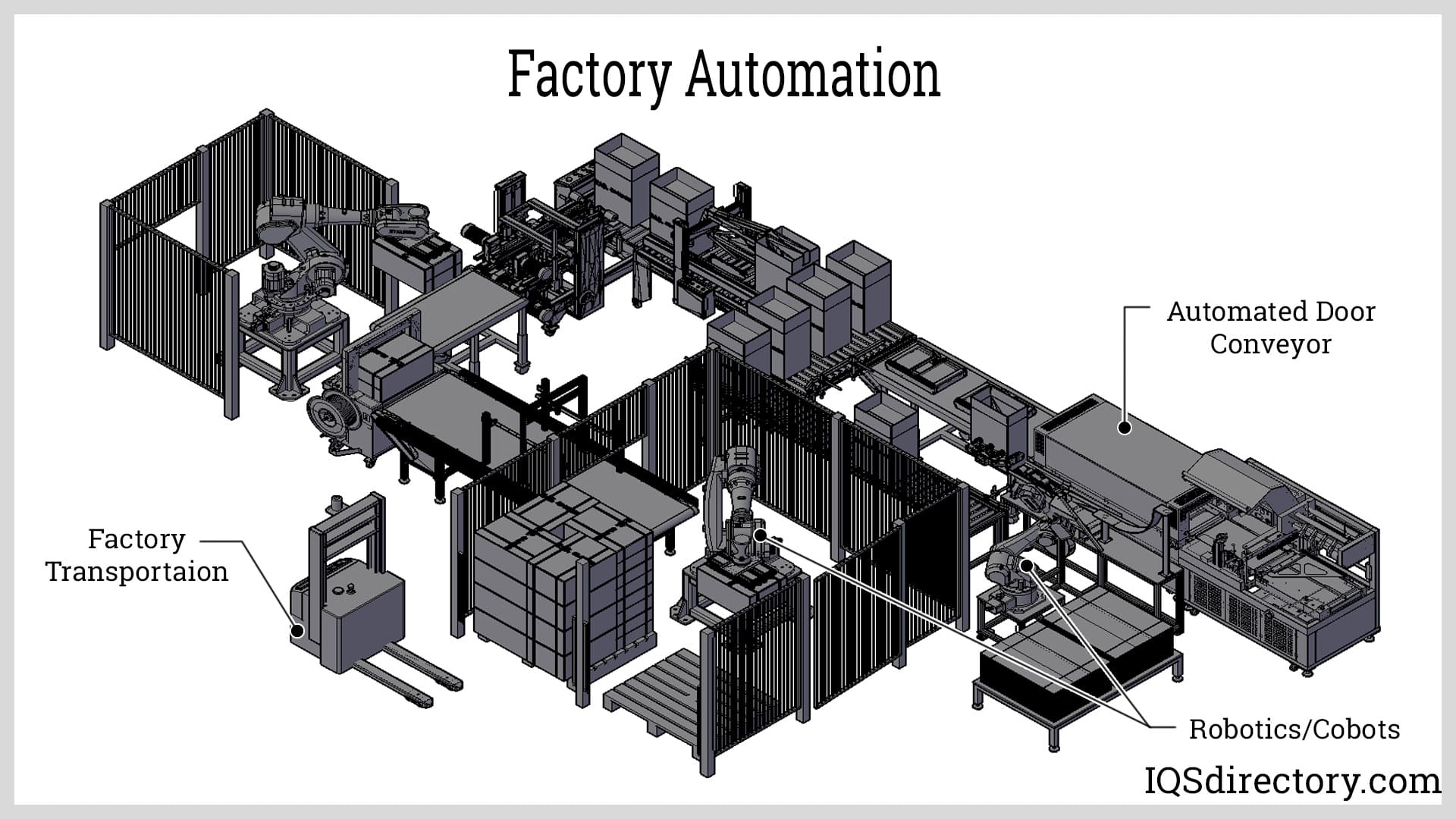
 AGVs
AGVs Casters
Casters Cranes
Cranes Conveyors
Conveyors Electric Hoists
Electric Hoists Forklifts
Forklifts Hydraulic Lifts
Hydraulic Lifts Platform Lifts
Platform Lifts Castings & Forgings
Castings & Forgings Bulk Material Handling
Bulk Material Handling Electrical & Electronic Components
Electrical & Electronic Components Flow Instrumentation
Flow Instrumentation Hardware
Hardware Material Handling Equipment
Material Handling Equipment Metal Cutting Services
Metal Cutting Services Metal Forming Services
Metal Forming Services Metal Suppliers
Metal Suppliers Motion Control Products
Motion Control Products Plant & Facility Equipment
Plant & Facility Equipment Plant & Facility Supplies
Plant & Facility Supplies Plastic Molding Processes
Plastic Molding Processes Pumps & Valves
Pumps & Valves Recycling Equipment
Recycling Equipment Rubber Products & Services
Rubber Products & Services